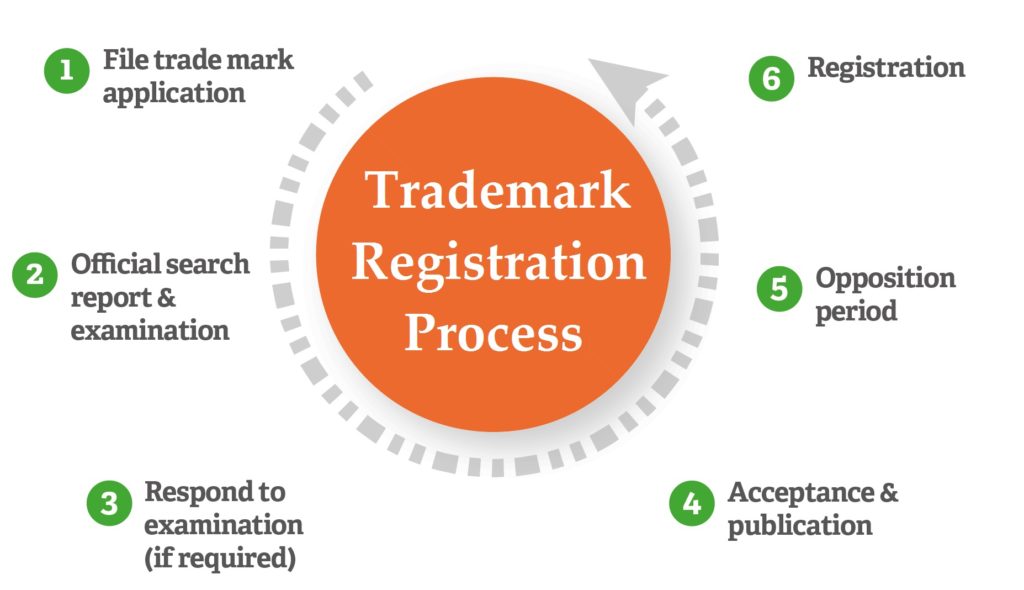
As per the NICHE classification, Trademark Classes are classified into 45 classes from which class 1 to 34 deals with the goods and class 35 to 45 deals with the services. Each of the trademark class represents a distinct set of goods and services. While filing a Trademark Application, the class of goods and services to which Trademark pertains must be mentioned in the Application. It is important to choose the right class of goods at the time of filing of the Application, otherwise choosing of wrong class of goods can hamper the whole registration process.
Trademark application can be filed in more than one class, if the business if the proprietor is involved in diverse. Further if Trademark is registered in one class, another entity can file a Trademark application in the another class. Filing of Trademark Application under one class does not give exclusivity to the person over the use of the mark. Trademark only gives exclusive right to use the mark to a person only in which class that mark is applied. Here is the list of trademark classes under from which product or services of a person will fall is described here as follows-
- Class 1- Chemical used in Industry, Science, photography, Agriculture, horticulture and Forestry; unprocessed plastics; chemical substances for preserving Foodstuffs.
- Class 2- Paints; Varnishes; Preservatives against rust and against deterioration of wood; colorants; metals in foil and powder form for painters; printer and artist.
- Class 3- Bleaching Preparations and substances for laundry use; cleaning; polishing; abrasive preparations; soaps; perfumery; essential oils; Cosmetics; hair lotions.
- Class 4- Industrial oil and greases; Lubricants; Dust absorbing; Wetting and Binding Compositions; Fuels ( including Motor Spirit) and illuminants; Candles; wicks.
- Class 5- Pharmaceutical, veterinary and Sanitary preparations; dietetic substances adapted for medical use; Food for babies; disinfectants; fungicides, herbicides.
- Class 6- Common Metals and their alloys; metal building material; small items for metal hardware; Pipes and tubes of metals; goods of metals not included in other classes.
- Class 7- Machine and machine tools; machine coupling and transmission components; agricultural implements other than hand operated; incubators for eggs.
- Section 8- Hand tools and implements ( Hand operated); Cutlery; side arms; razors.
- Section 9- Scientific, electric, Photographical, measuring, apparatus for recording, transmission or reproduction of sound or images; data processing equipment and computers.
- Class 10- Surgical, Medical, dental and veterinary apparatus and instruments’ artificial limbs, eyes and teeth; orthopaedic articles; suture materials.
- Class 11- apparatus for lighting, heating, steam generating, cooking, refrigerating, drying ventilating; water supply and sanitary purposes.
- Class 12- vehicles; apparatus for locomotion of land, air or water.
- Class 13- Firearms; ammunition and projectiles; explosives; fire works.
- Class 14- Precious metals and their alloys and goods in precious metals; jeweller, precious stones; horological and other chronometric instruments.
- Class 15- Musical Instruments
- Class 16- Paper, cardboard and goods made from these materials; printed matter; stationary; brushes; typewriters and office requisites; plastic materials for packaging.
- Class 17- Ruber, asbestos, mica and goods made from these materials; Plastics in extruded form for use in manufacture; pack=king; stopping and insulating materials; flexible pipes.
- Class 18- Leather and imitations of leather; animal skins, hides, trunks and travelling bags; umbrellas, parasols and walking sticks; whips; harness and saddlery.
- Class 19- Building Materials ( non- metallic), Non- metallic rigid pipes for building; asphalt; pitch and bitumen; non- metallic transportable buildings; monuments not of metals.
- Class 20- Furniture, mirrors, picture frames; goods of wood, cork, reed, cane, whicker, horne, bone, ivory, whalebone, shll, amber, mother of pearl, meerschaum or of plastic.
- Class 21- Household or kitchen utensils and containers; combs and sponges; articles for cleaning purposes; unworked or semi worked glass; glassware and earthenware.
- Class 22- Ropes, strings, nets, tents, awnings, tarpaulins, sails, sacks and bags, paddling and stuffing materials (Except rubber or plastics); raw fibrous textile materials.
- Class 23- Yarns and threads, for textile use.
- Class 24- Textile and textile goods, not included in other classes; bed and table cover.
- Class 25- Clothing, footwear and headgear.
- Class 26- Lace and embroidery, ribbons and braids; button, hooks and eyes, pins and needles; Artificial flowers.
- Class 27- carpets, rugs, mats and matting; linoleum and other materials for covering existing floors; wall hanging (Non-textile).
- Class 28- Games and playthings, gymnastic and sporting articles not included in other classes; decorations for christmas trees.
- Class 29- Meat, fish, poultry and game; meat extracts; preserved, dried and cooked fruits and vegetables; jams, fruits sauces; eggs, milk and milk products; edible oils and fats.
- Class 30- Coffee, tea, cocoa, sugar, rice, tapioca, sago; bread, pastry and confectionery, ices; honey, treacle; yeast, baking powder; salt, mustard ; vinegar; spices; ice.
- Class 31- Agricultural, horticultural and forestry products and grains; Live animals; fresh fruits and vegetables; seeds, natural plants and flowers; food stuff for animals and malt.
- Class 32- Beers, minerals and aerated waters, and other non alcoholic drinks; fruit drinks and fruits juices; syrups and other preparations for making beverages.
- Class 33- Alcoholic Beverages (Except beers).
- Class 34- Tobacco, smokers’ articles, ,matches.
- Class 35- Advertising, business management, business administration, Office functions.
- Class 36- Insurance, Financial affairs; monetary affairs; real estate affairs.
- Class 37- Building construction; repair; installation services.
- Class 38- Telecommunications.
- Class 39- Transport, packaging and storage of goods; travel arrangement.
- Class 40- Treatment of materials.
- Class 41- Education; Providing of training; entertainment; sporting and cultural activities.
- Class 42- scientific, design and technological services; industrial analysis and research services; design and development of computer hardware and software.
- Class 43- Services for providing food and drink; temporary accommodation.
- Class 44- Medical services; veterinary services; hygienic and beauty care for human beings or animals; agriculture, horticulture and forestry services.
Class 45- Legal services; security services for the protection of property and individuals; personal and social services rendered by others to meet the needs of the individuals.